The Power of AI Agents: Overcoming LLM Limitations for Real-World Solutions
LLMs are powerful but raw LLMs have limitations: they can be poor at math, hallucinate information, are stateless (lack memory), and cannot access real-time info. To overcome these gaps, AI Agents play a pivotal role, turning language models into practical problem solvers.
What is an AI Agent?
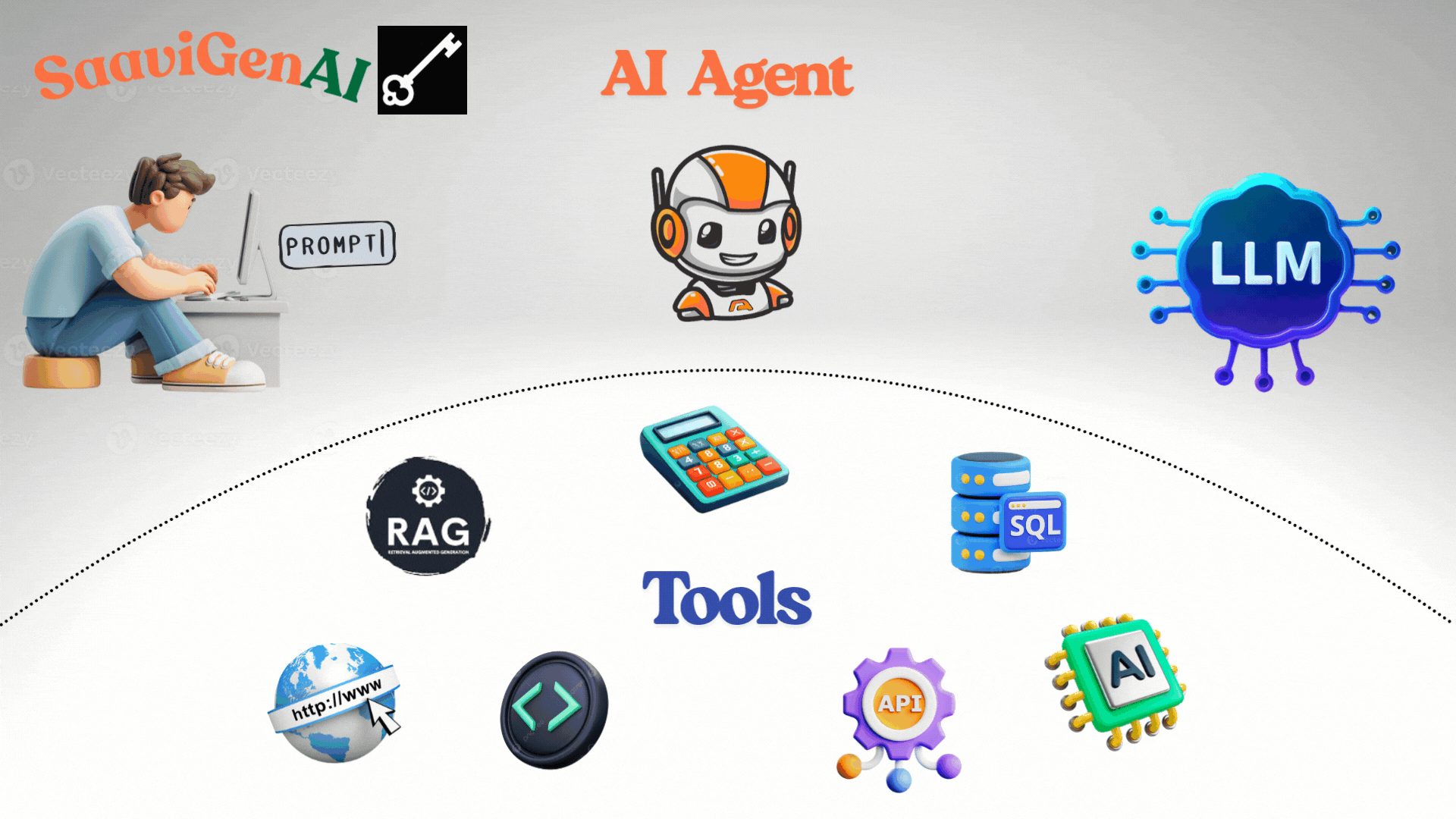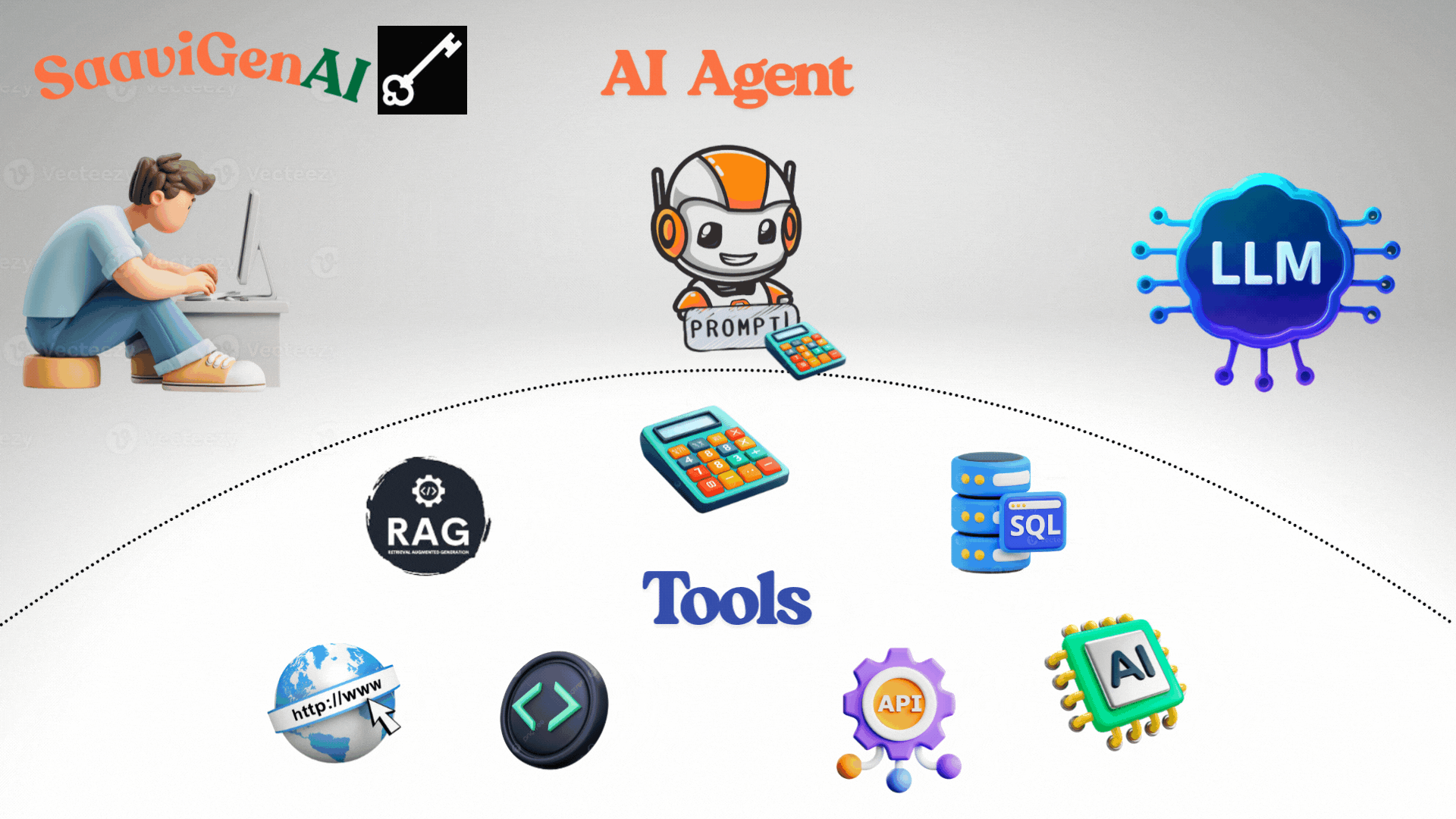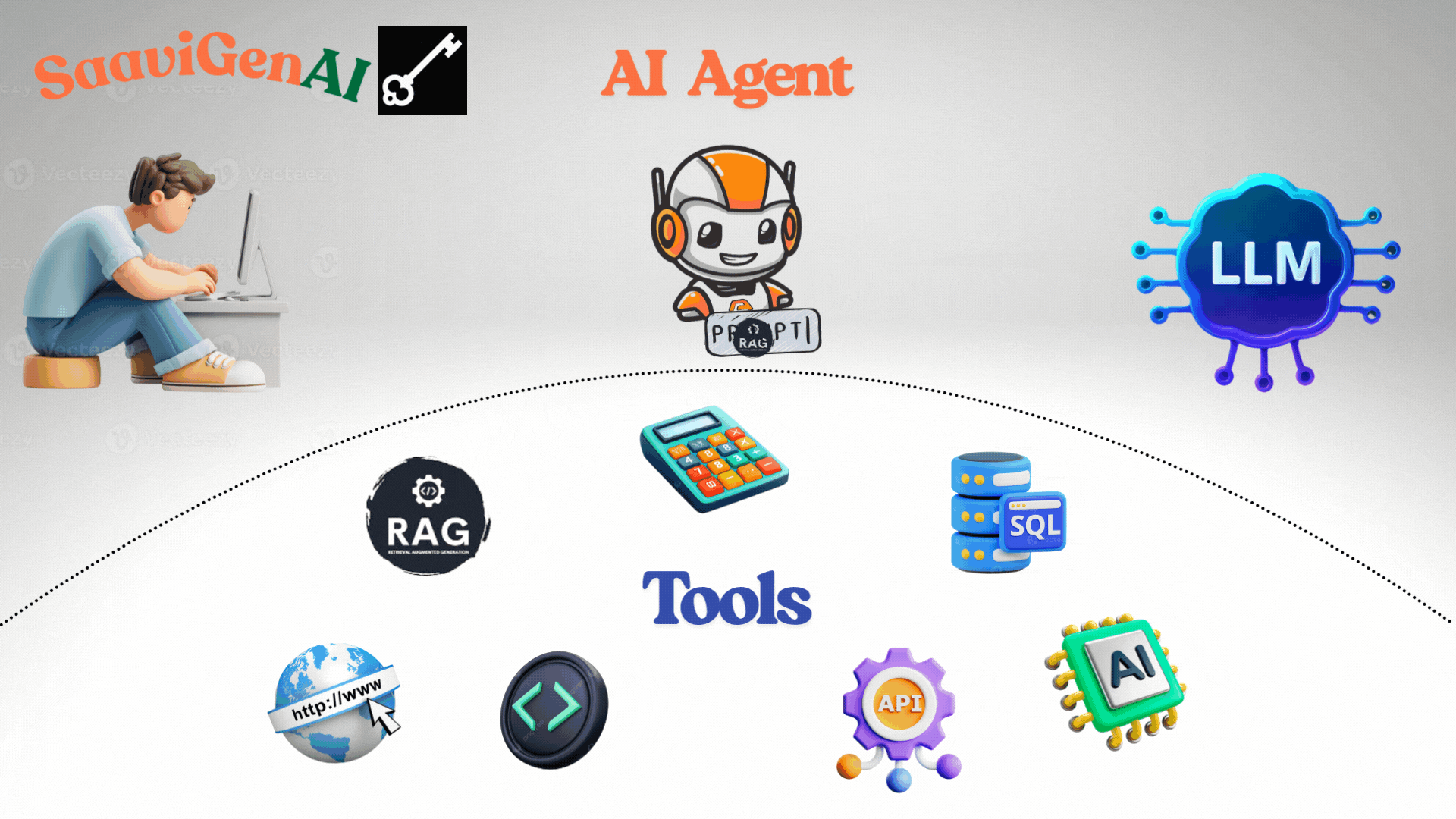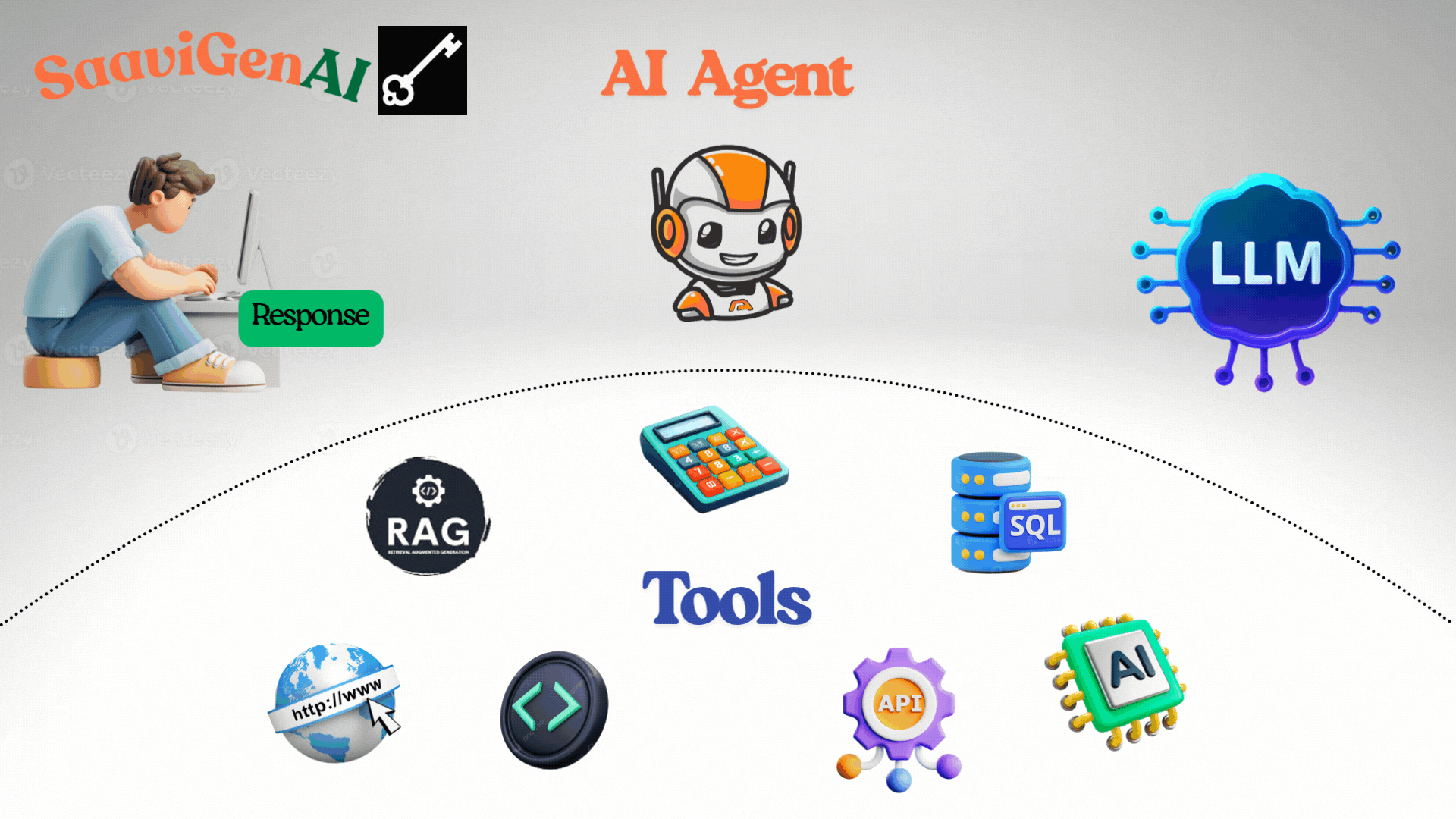
An AI Agent is an intelligent software system that uses artificial intelligence to autonomously reason, plan, and act in pursuit of specific goals. Unlike basic LLMs, an agent interacts with external tools, remembers previous actions and decisions, and adapts as it works toward your desired outcome. It thinks step-by-step, much like a digital assistant that can use calculators, web browsers, databases, and more to solve real-world problems.
How AI Agents Work: The ReAct Framework
The ReAct Agent is one of the most popular frameworks. It operates in cycles of:
- Thought: The agent understands the user's request and determines what to do next.
- Action: It selects and uses the most appropriate tool (like a calculator or search engine).
- Observation: It reviews the result—did the tool provide what was needed?
This process repeats until the goal is achieved.
Example: Adding Two Numbers
- User Request: "What is 25 + 37?"
- Thought: "This is an addition problem; I should use the calculator tool."
- Action: Uses calculator tool for 25 + 37.
- Observation: Gets the result: 62.
- Final Response: "25 + 37 = 62."
This simple cycle is the foundation for much bigger tasks, enabling agents to handle complex workflows by stringing together reasoning, tool use, and observations.
Tools Used by AI Agents
For advanced capability, AI Agents connect with a wide range of tools, including:
- Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG): Fetches knowledge from databases, documents, and past conversations.
- Memory Systems: Supplies both short-term memory (current context) and long-term memory (persistent knowledge).
- Calculators & Code Interpreters: Handles math, logic, and programming tasks.
- Search Engines/Internet: Accesses up-to-date information and facts.
- APIs: Integrates with external services (emails, calendars, data providers).
- Databases: Queries structured data for insights and records.
- Other AI Models: Uses specialized AI for vision, speech, or domain-specific reasoning.
This toolset empowers agents with extra intelligence and flexibility far beyond what a pure LLM offers.
Types of AI Agents
There are several main types of AI Agents:
- Conversational Agents: Chatbots and virtual assistants focused on dialogue and answers.
- Task-Specific Agents: Specialized for functions like customer service, research, or data analysis.
- Multi-Agent Systems: Multiple agents collaborate, each with unique skills (e.g., one searches, one calculates).
- Autonomous Agents: Capable of independent, long-running problem solving with minimal human intervention.
Each type varies by domain knowledge, memory depth, and integration with tools.
Getting Started with AI Agents
If you're new to AI Agents, practical steps include:
- Use Existing Platforms: Try ChatGPT plugins, Claude, Bard, or browser-based AI assistants to see agent behavior.
- Learn Prompt Engineering: Craft clear, goal-driven requests—better prompts yield smarter results.
- Explore Development Frameworks: Frameworks like LangChain, AutoGen, or n8n let you build custom agents with plug-in tools and memory.
- Start Simple: Experiment with basic tasks (math, reminders) before tackling complex flows (research, automation).
- Follow AI News: Stay updated; this field evolves rapidly, with new capabilities arriving every month.
Conclusion
AI Agents are transforming the way we harness artificial intelligence. By connecting reasoning engines with toolkits and memory, they solve practical problems that classical LLMs can't handle. Whether answering simple math or orchestrating a multi-step workflow, agents make AI truly useful. For beginners, understanding these essential concepts unlocks new opportunities—AI Agents are the future of intelligent digital assistants.